Accessing the Knowledge Center effectively requires a simple, one-time registration.
Zoom on turbo technology | BOOSTING THE FUTURE
Turbos are fundamental to addressing the auto industry’s most pressing challenges. They dramatically improve combustion process efficiency, enhance vehicle performance and help reduce emissions. No wonder more than 140 million Garrett turbos currently boost cars and trucks around the world. Please also see our basic, expert and advanced guides on how turbo works.
What Is a Turbo and How Does It Work? – Knowledge Guide
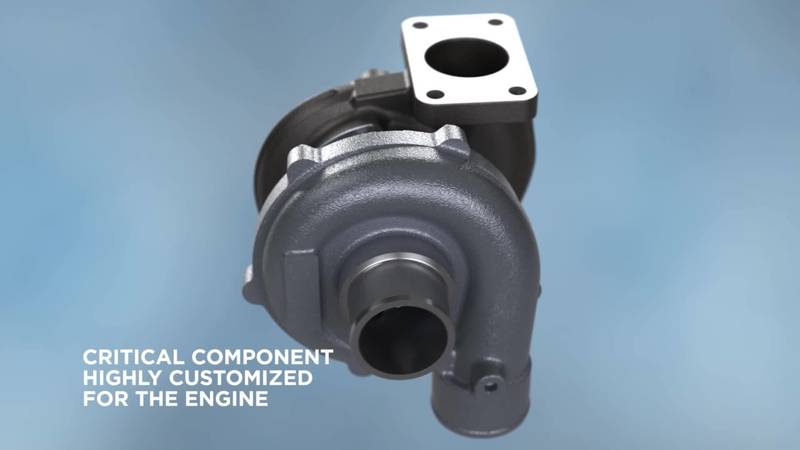
A turbocharger is a critical component highly customized for the engine. It uses an engine’s exhaust gas to drive the turbine wheel up to 350,000 RPM.
The turbine wheel then drives the compressor wheel through a shaft. The compressor wheel provides compressed air to the engine, and this compressed-air makes the fuel burn more efficiently for greater power and fuel economy.
Up to 1900 Fahrenheit
Up To 350,000 RPM
1,900 km/h
1,100 mph
Turbos utilize exhaust gases to power a turbine wheel, which is connected via a shaft to a compressor wheel. As the two wheels turn, large amounts of ambient air are sucked in and compressed. This air is passed through a charge-air cooler to further increase its density before it enters the engine.
Turbocharged engines generate more power than naturally-aspirated engines of the same size. And the combustion process becomes more efficient. Furthermore, this helps reduce emissions and enhance the driving experience.
A turbocharger is highly engineered with high-value components. The next step is e-boosting with advanced power electronics.
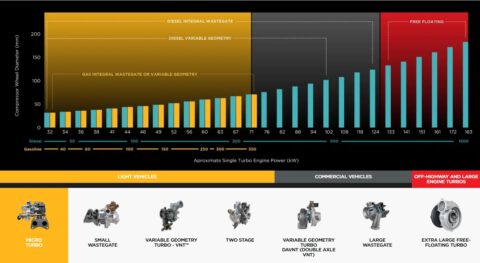
BROADEST TURBO COLLECTION
For The Widest Engine Range
Garrett’s turbo portfolio covers the widest engine range in the automotive industry. From micro turbos for small cars to large turbos for off-highway equipment, Garrett’s line-up offers the world’s auto manufacturers boosting solutions for gasoline, diesel, CNG, hybrid powertrains and hydrogen fuel cells.
TURBO INSIGHTS
Knowledge Booster
Browse our turbo resources to boost your knowledge base.

















